GASTROENTEROLOGY
Clinical experience of PEG tube insertion in the clinical setting
The crucial decision on PEG tube insertion lies on the risks and benefits of each specific situation
September 7, 2016
-
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) tube is an important means to provide enteral nutrition in a selected subgroup of patients. The decision for PEG insertion is usually made after a clear multidisciplinary discussion with patients and families. There are many medical conditions that would warrant consideration for PEG feeding, but the crucial decision lies on the risks and benefits of each specific situation with full involvement and discussion by physicians with patients and families. Multidisciplinary care and educational programmes have been found to reduce the numbers of patients receiving feeding tubes inappropriately.1
The American Medical Directors Association, American Geriatrics Society and American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine recommend against inserting PEG in individuals with advanced dementia and instead, recommend oral assisted feedings.2,3,4
Aims and methods
This retrospective study aimed to assess the patient cohort in Connolly Hospital, Blanchardstown, Dublin who have had a PEG tube inserted endoscopically between January 2014 and August 2015.
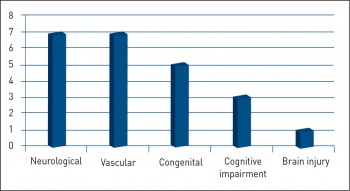
We evaluated the indications, specialty of physicians involved, time frame between presentation of illness to PEG insertion, patient age, sedation used and any immediate complications related to the procedure.
We obtained data from the EndoRAAD database (endoscopy reporting system), medical chart review and phone contact to relatives and general practitioners.
Results
A total of 23 patients had PEG inserted endoscopically, 13 females (56.5%) and 10 males (43.5%) as compared to 27 patients in the previous 20 months. Comparatively, there were six cases of radiologically inserted gastrostomy (RIG) during the corresponding 20 month period. The average age was 65 years (32-87). The average midazolam dose was 3.75mg, fentanyl 50mcg and pethidine 25mg. There were no documented immediate complications (see Figure 1).
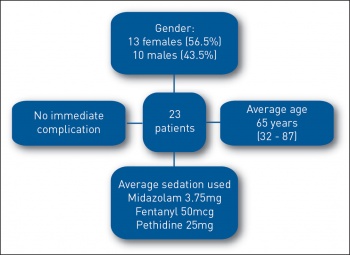 Figure 1. PEG study data(click to enlarge)
Figure 1. PEG study data(click to enlarge)